How to read XML file in Python
XML, or Extensible Markup Language, is a markup-language that is commonly used to structure, store, and transfer data between systems.
The process of reading the data from an XML file and analyzing its logical components is known as Parsing.
In this article, we would take a look at the library that could be used for the purpose of xml parsing. It is BeautifulSoup used alongside the lxml xml parser
BeautifulSoup alongside with lxml parser
BeautifulSoup is a Python library for reading and writing XML file. Type the following command into the terminal to install this.
pip install beautifulsoup4
Beautiful Soup supports the HTML parser included in Python’s standard library, but it also supports a number of third-party Python parsers. One is the lxml parser (used for parsing XML/HTML documents). lxml could be installed by running the following command:
pip install lxml
Reading an XML file includes two steps; Finding Tags and Extracting from tags
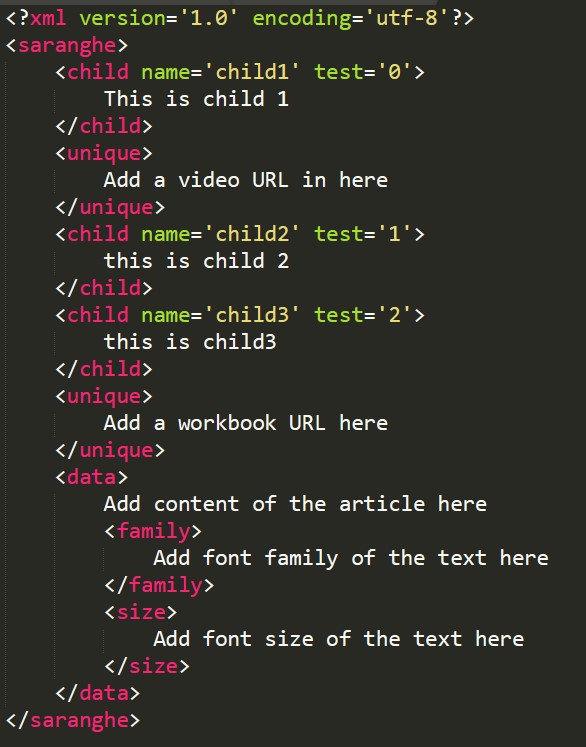
The XML file used in this article is
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
# Reading the data inside the xml file
with open('test.xml', 'r') as f:
data = f.read()
# Passing the stored data inside the beautifulsoup parser
Bs_data = BeautifulSoup(data, "xml")
# Finding all instances of tag
# `unique`
b_unique = Bs_data.find_all('unique')
print(b_unique)
# Using find() to extract attributes
# of the first instance of the tag
b_name = Bs_data.find('child', {'name':'child1'})
print(b_name)
# Extracting the data stored in a
# specific attribute of the
# `child` tag
value = b_name.get('test')
print(value)
Output:
[<unique> Add a video URL in here </unique>, <unique> Add a workbook URL here </unique>] <child name="child1" test="0"> This is child 1 </child> 0
